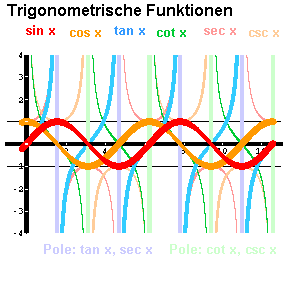
y = cos x
y = tan x
y = cot x
y = sec x
y = csc x
sin x = a / r
cos x = b / r
tan x = a / b
cot x = b / a
sec x = r / b
csc x = r / a
r : Radius, Hypothenuse
a : Gegenkathete
b : Ankathete
r = 1 : Einheitskreis
y = arccos x
y = arctan x
y = arccot x
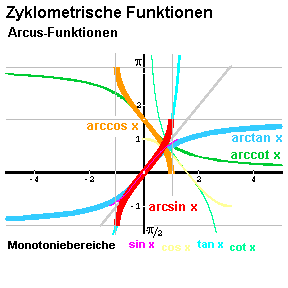
(in einem Monotoniebereich):
x = sin y (mit |x| ≤ 1 )
x = cos y (mit |x| ≤ 1 )
x = tan y
x = cot y
cos u
tan u
cot u
sec u
csc u
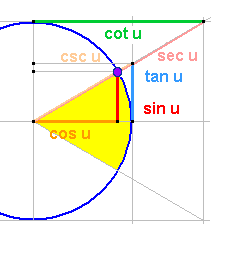
u : Fläche des Segments (gelb : gelb)
u : (ebenso) halber Öffnungswinkel
sin u : Vertikalwert Kreisschnittpunkt
cos u : Horizontalwert Kreisschnittpunkt
tan u : Abschnitt auf Vertikaltangente
(Vertikaltangente: x = r )
cot u : Abschnitt auf Horizontaltangente
(Horizontaltangente: y = r )
sec u : Radialabschnitt bis Horizontaltangente
csc u : Radialabschnitt bis Vertikaltangente
r = 1 (Radius des Einheitskreises)
y = cosh x
y = tanh x
y = coth x
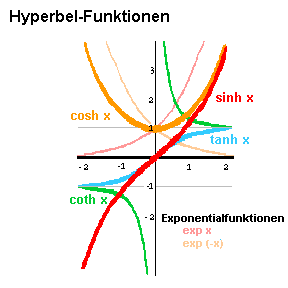
sinh x = ( ex - e-x ) / 2
cosh x = ( ex + e-x ) / 2
tanh x = sinh x / cosh x
coth x = 1 / tanh x
y = arcosh x
y = artanh x
y = arcoth x
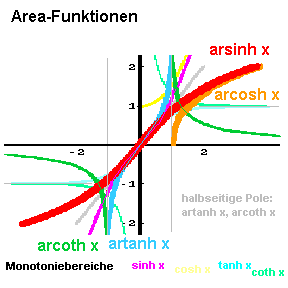
(in einem Monotoniebereich):
x = sinh y
x = cosh y (mit x ≥ 1 )
x = tanh y (mit |x| < 1 )
x = coth y (mit |x| > 1 )
cosh u
tanh u
coth u
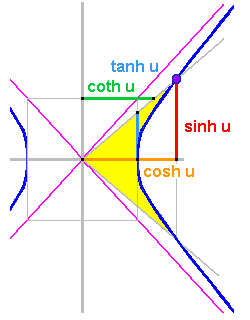
u : Fläche des Segments (gelb : gelb)
sinh u : Vertikalwert Hyperbelschnittpunkt
cosh u : Horizontalwert Hyperbelschnittpunkt
tanh u : Abschnitt auf Vertikaltangente
(Vertikaltangente: x = a )
coth u : Abschnitt (virt.) Horizontaltangente
(Horizontaltangente: y = b )
a = b = 1 (Halbachsen der Einheitshyperbel)
mit Hyperbel-Asymptoten